引用FFTW3读取并估计wav文件音频的基频
接上一篇《不引用第三方库读取wav文件并逐帧估算基频》,这里引用了第三方专用库FFTW3,实现同样的功能。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <fftw3.h>
#pragma comment( lib, "libfftw3-3.lib")
#pragma comment( lib, "libfftw3f-3.lib")
#pragma comment( lib, "libfftw3l-3.lib")
// WAV文件头结构
typedef struct {
char riff[4];
uint32_t overall_size;
char wave[4];
char fmt_chunk_marker[4];
uint32_t length_of_fmt;
uint16_t format_type;
uint16_t channels;
uint32_t sample_rate;
uint32_t byte_rate;
uint16_t block_align;
uint16_t bits_per_sample;
char data_chunk_header[4];
uint32_t data_size;
} WAV_HEADER;
// 读取WAV文件头
WAV_HEADER read_wav_header(FILE* file) {
WAV_HEADER header;
fread(&header, sizeof(WAV_HEADER), 1, file);
return header;
}
// 读取WAV文件的音频数据
float* read_wav_data(FILE* file, WAV_HEADER header, int* num_samples) {
int data_size = header.data_size / (header.bits_per_sample / 8);
float* data = (float*)malloc(data_size * sizeof(float));
short int* temp = (short int*)malloc(header.data_size);
fread(temp, sizeof(short int), header.data_size / sizeof(short int), file);
for (int i = 0; i < data_size; i++) {
data[i] = (float)temp[i] / 32768.0; // 假设是16位PCM编码,范围是-32768到32767
}
free(temp);
*num_samples = data_size;
return data;
}
// 估算基频(简单峰值检测)
double estimate_fundamental_frequency(fftw_complex* out, int N, double sample_rate) {
double max_magnitude = 0.0;
int max_index = 0;
// 查找FFT结果中的最大峰值(除了直流分量)
for (int i = 1; i < N / 2; i++) {
double magnitude = sqrt(out[i][0] * out[i][0] + out[i][1] * out[i][1]);
if (magnitude > max_magnitude) {
max_magnitude = magnitude;
max_index = i;
}
}
// 计算基频
double fundamental_frequency = (double)max_index * (sample_rate / N);
return fundamental_frequency;
}
// 自定义基频估算函数(简单峰值检测)
double custom_estimate_fundamental_frequency(fftw_complex* out, int N, double sample_rate) {
double max_magnitude = 0.0;
int max_index = 0;
int start_index = N / (sample_rate / 10.0); // 假设我们只对10Hz到采样率一半之间的频率感兴趣
int end_index = N / 2; // FFT结果的对称性,只考虑前半部分
// 查找FFT结果中的最大峰值(在指定范围内)
for (int i = start_index; i < end_index; i++) {
double magnitude = sqrt(out[i][0] * out[i][0] + out[i][1] * out[i][1]);
if (magnitude > max_magnitude) {
max_magnitude = magnitude;
max_index = i;
}
}
// 如果找到了峰值,则计算对应的频率
if (max_index > 0 && max_index < end_index) {
double fundamental_frequency = (double)max_index * (sample_rate / N);
return fundamental_frequency;
}
else {
// 如果没有找到明显的峰值,则返回0或某个表示未找到基频的值
return -1.0; // 这里返回-1表示未找到基频,实际应用中可以根据需要调整
}
}
// 自定义基频估算函数(简单峰值检测)
double estimate_fundamental_frequency(double* magnitudes, int N, double sample_rate) {
double max_magnitude = 0.0;
int max_index = 0;
int start_index = N / (sample_rate / 10.0); // 假设我们只对10Hz到采样率一半之间的频率感兴趣
int end_index = N / 2; // FFT结果的对称性,只考虑前半部分
// 查找FFT结果中的最大峰值(在指定范围内)
for (int i = start_index; i < end_index; i++) {
if (magnitudes[i] > max_magnitude) {
max_magnitude = magnitudes[i];
max_index = i;
}
}
// 如果找到了峰值,则计算对应的频率
if (max_index > 0 && max_index < end_index) {
double fundamental_frequency = (double)max_index * (sample_rate / N);
return fundamental_frequency;
}
else {
// 如果没有找到明显的峰值,则返回0或某个表示未找到基频的值
return -1.0; // 这里返回-1表示未找到基频,实际应用中可以根据需要调整
}
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {
//if (argc != 2) {
// fprintf(stderr, "Usage: %s <wav_file>\n", argv[0]);
// return 1;
//}
FILE* file = fopen("wdsyy1.wav", "rb");
if (!file) {
perror("Failed to open file");
return 1;
}
WAV_HEADER header = read_wav_header(file);
// 检查是否是PCM编码的WAV文件
if (header.format_type != 1) {
fprintf(stderr, "Unsupported WAV format\n");
fclose(file);
return 1;
}
int num_samples;
float* data = read_wav_data(file, header, &num_samples);
fclose(file);
// 设置FFT大小(通常是2的幂)
int N = 1024; // 可以根据需要调整
while (N < num_samples) N *= 2;
// 为FFT准备输入和输出数组
fftw_complex* in = (fftw_complex*)fftw_malloc(sizeof(fftw_complex) * N);
fftw_complex* out = (fftw_complex*)fftw_malloc(sizeof(fftw_complex) * N);
//fftw_plan plan = fftw_plan_dft_r2c_1d(N, (double*)data, out, FFTW_ESTIMATE);
//fftw_plan plan = fftw_plan_dft_1d(N, in, out, FFTW_ESTIMATE);
// 将音频数据填充到FFT输入数组中(注意:只填充前num_samples个值,其余置零)
for (int i = 0; i < num_samples; i++) {
in[i][0] = data[i];
in[i][1] = 0.0;
}
for (int i = num_samples; i < N; i++) {
in[i][0] = 0.0;
in[i][1] = 0.0;
}
fftw_plan plan = fftw_plan_dft_1d(N, in, out, FFTW_FORWARD, FFTW_ESTIMATE);
// 执行FFT
fftw_execute(plan);
// 计算FFT结果的幅度
double* magnitudes = (double*)malloc(sizeof(double) * (N / 2 + 1));
for (int i = 0; i <= N / 2; i++) {
magnitudes[i] = sqrt(out[i][0] * out[i][0] + out[i][1] * out[i][1]);
}
// 估算基频
//double fundamental_frequency = estimate_fundamental_frequency(out, N, header.sample_rate);
//double fundamental_frequency = custom_estimate_fundamental_frequency(out, N, header.sample_rate);
// 估算基频
double fundamental_frequency = estimate_fundamental_frequency(magnitudes, N, header.sample_rate);
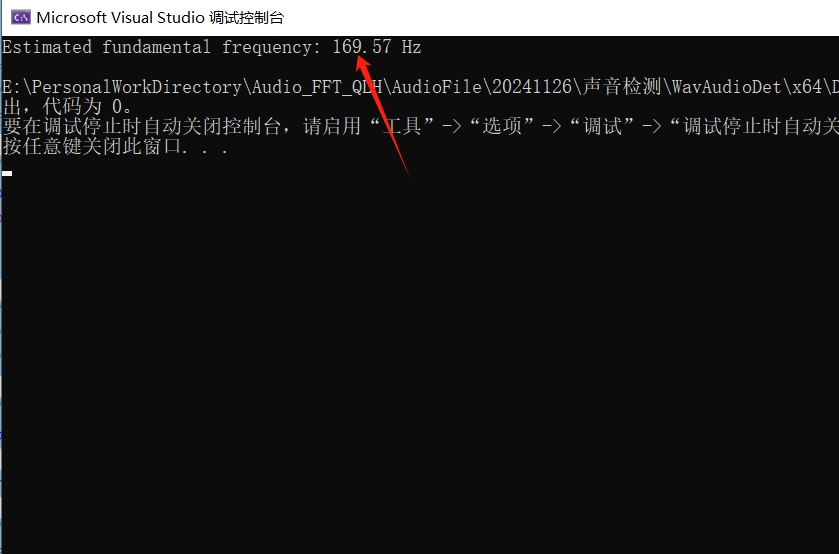
printf("Estimated fundamental frequency: %.2f Hz\n", fundamental_frequency);
// 清理
fftw_destroy_plan(plan);
fftw_free(in);
fftw_free(out);
free(data);
return 0;
}运行结果
FFTW3库文件(头文件,lib,dll)
X64由于文件超大了,所以分开了,下载后放到一起即可。
凯特网版权声明:以上内容允许转载,但请注明出处,谢谢!

